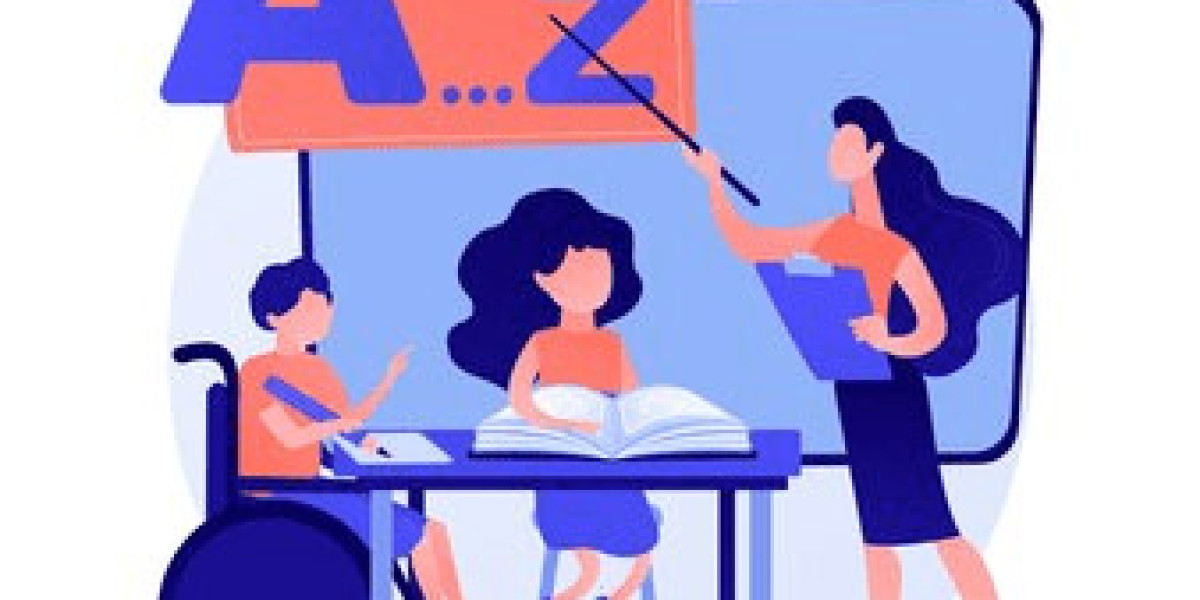
Intellectual disability is a condition characterized by significant limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior, affecting everyday social and practical skills. This condition originates before the age of 18 and impacts learning, problem-solving, and everyday tasks. Support and tailored interventions can help individuals with intellectual disabilities lead fulfilling lives. Services like those offered by TalktoAngel provide guidance and support for individuals and their families, helping them develop coping strategies, access resources, and enhance their quality of life.
What is an example of an intellectual disability?
One illustration of an intellectual disability. Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21. Individuals with Down syndrome often experience developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and distinct physical features. They may require support in learning, communication, and daily activities. With appropriate care and resources, people with Down syndrome can lead fulfilling and productive lives.
What Are the Most Common Causes of Intellectual Disability?
Seeking professional guidance"Therapist near me" ensures that individuals with intellectual disabilities receive tailored support and effective interventions. Personalized support helps families navigate challenges and maximize the potential of their loved ones.
Genetic Conditions: Conditions such as Down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome, and Phenylketonuria (PKU).
Metabolic Disorders: Issues with the body’s metabolism, such as untreated hypothyroidism.
Brain Malformations: Abnormal development of the brain, such as microcephaly or lissencephaly.
Maternal Infections During Pregnancy: Infections like rubella, cytomegalovirus, or Zika virus.
Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to alcohol (fetal alcohol syndrome), drugs, or environmental toxins during pregnancy.
Malnutrition: Poor nutrition during pregnancy leading to developmental issues.
Complications During Birth: Oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) or trauma during birth.
Premature Birth: Being born significantly preterm and associated complications.
Low Birth Weight: Weighing less than 2,500 grams (5.5 pounds) at birth.
Childhood Diseases: Infections like meningitis or encephalitis during early childhood.
Severe Head Injury: Traumatic brain injury during childhood.
Neglect or Abuse: Severe emotional or physical neglect or abuse during early childhood.
Severe Malnutrition: Inadequate nutrition during early developmental years.
Environmental Toxins: Exposure to lead, mercury, or other toxic substances during childhood.
Unknown Causes: In some cases, the cause of intellectual disability may not be identified, despite thorough investigation.
If anyone is struggling with intellectual disabilities, along with their families, "Best counsellor "offers accessible and personalized support, opening up new avenues for assistance.
How to Support Someone with Intellectual Disability?
Supporting someone with an intellectual disability involves understanding their needs and providing appropriate assistance. Here are to consider:
Educate Yourself: Learn about intellectual disabilities to better understand their challenges and strengths.
Show Patience: Be patient and give them time to express themselves and complete tasks.
Communicate Clearly: Use simple, clear language and repeat information if necessary.
Encourage Independence: Foster independence by encouraging them to do tasks on their own with minimal assistance.
Provide Structure: Establish a routine to create a sense of stability and predictability.
Be Supportive: Offer emotional support and be understanding of their feelings and experiences.
Promote Social Inclusion: Encourage social interactions and participation in community activities.
Use Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and celebrate their achievements to build confidence.
Adapt Learning Materials: Use visual aids and hands-on activities to facilitate learning.
Assist with Decision Making: Help them make decisions by providing options and discussing potential outcomes.
Create a Safe Environment: Ensure their living and working spaces are safe and accessible.
Set Realistic Goals: Help set achievable goals and provide support to reach them.
Encourage Hobbies and Interests: Support involvement in activities they enjoy to promote engagement and happiness.
Seek Professional Help: Utilize the services of therapists, counselors, and other professionals for specialized support.
Advocate for Their Rights: Stand up for their rights and ensure they have access to necessary resources and opportunities.
In conclusion, intellectual disability is a complex condition that can impact individuals and their families in various ways.