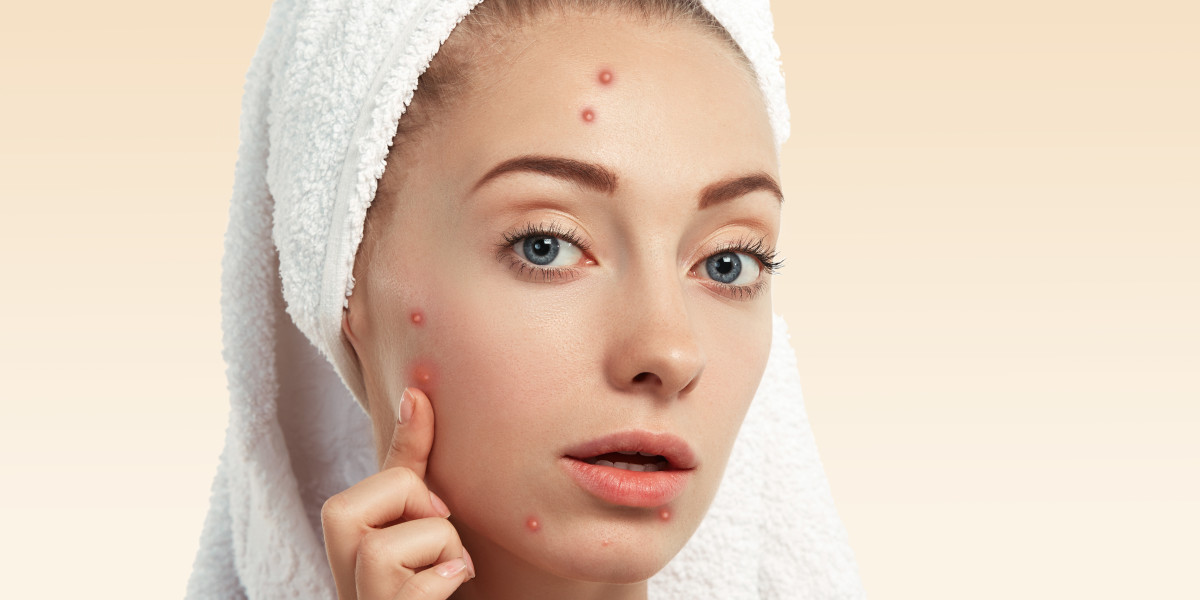
Fungal acne, despite its name, isn't actually acne in the traditional sense. It's a skin condition caused by an overgrowth of yeast, specifically Malassezia, which is naturally present on the skin. Understanding its appearance and symptoms is crucial for proper identification and treatment. Buy Accutane online for perfect acne treament. Here’s what you need to know about fungal acne and how to recognize it.
Appearance and Symptoms
1. Small, Uniform Bumps: Fungal acne typically presents as small, uniform bumps that are often mistaken for regular acne. These bumps can be itchy and are commonly found on the chest, back, and shoulders, although they can also appear on the face. Unlike bacterial acne, which can vary in size and shape, the bumps caused by fungal acne are usually all the same size.
2. Clusters of Pimples: One of the distinguishing features of fungal acne is the way it forms in clusters. These clusters can appear as grouped pimples that resemble a rash. This clustering is due to the yeast's tendency to multiply quickly in certain areas.
3. Itchiness: Fungal acne is often itchy, which is a key differentiator from bacterial acne. If you experience persistent itchiness along with the appearance of pimples, it could be a sign of a fungal infection.
4. Location: While fungal acne can occur on the face, it's more commonly found on the body, particularly in areas that are prone to sweat and moisture, such as the chest, back, and shoulders. The yeast thrives in warm, humid environments, making these areas ideal for growth.
5. Lack of Blackheads and Whiteheads: Traditional acne often features blackheads and whiteheads, which are clogged pores filled with sebum and dead skin cells. Fungal acne, on the other hand, does not typically include these features. Instead, it manifests as red, inflamed bumps.
Causes and Triggers
1. Sweating and Humidity: Excessive sweating and exposure to humid environments can promote the growth of Malassezia yeast. Wearing tight clothing that doesn't allow the skin to breathe can exacerbate the condition.
2. Antibiotic Use: Long-term use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria on the skin, allowing yeast to overgrow and cause fungal acne.
3. Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to fungal infections, including fungal acne.
4. Oily Skin: Oily skin can provide an ideal environment for yeast to thrive, increasing the likelihood of developing fungal acne.
Treatment Options
1. Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal treatments, such as shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide, can be effective. These can be applied to the affected areas and left on for a few minutes before rinsing off.
2. Prescription Treatments: In more severe cases, a healthcare provider might prescribe oral medications like isotretinoin 20mg to combat the infection from within.
3. Good Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper hygiene, including regular showering and wearing breathable clothing, can help manage and prevent fungal acne. It's also important to keep the skin dry and avoid environments that promote excessive sweating.
4. Avoiding Oily Products: Using non-comedogenic skincare products that don't add excess oil to the skin can help keep fungal acne at bay.
Conclusion
Fungal acne can be frustrating due to its persistent itchiness and tendency to mimic regular acne. However, understanding its unique characteristics—such as small, uniform bumps, itchiness, and clustering—can aid in proper identification and treatment. If you suspect you have fungal acne, consult with a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan. With the right approach, you can manage this condition and maintain healthy, clear skin.